How long should it take to evacuate your premises in the event of a fire?
Fire safety practitioners are often asked, particularly after a fire drill, how long it should take to evacuate the premises.
What, on the face of it, appears to be a simple question has quite a complex answer, particularly in view of the UK’s risk-based fire safety regime.
Those responsible for fire safety need to know what would be deemed to be a safe evacuation time and the factors that influence this.
Legislation, such as the Regulatory Reform (Fire Safety) Order 2005 (RRFSO), does not prescribe any evacuation times. Rather, the RRFSO states that “in the event of danger, it must be possible for persons to evacuate the premises as quickly and as safely as possible”.
The reason for this is that, unlike fire certification arrangements under the old regime, where each certificate was building specific, the RRFSO applies to a wide range of buildings, therefore making it impossible to prescribe evacuation times.
Guidance to the RRFSO does contain further information on evacuation times. For example, guidance for office environments notes that “escape routes in a building should be designed so that people can escape quickly enough to ensure they are not placed in any danger from fire”.
The key phrase here is “should be designed”. This clearly indicates that designers of buildings need to consider the design of the means of escape as part of the overall design of the property so that occupants can move to a place of reasonable and/or total safety before the conditions in the property become untenable.
Certainly, designers should be following the requirements of the respective Building Regulations and associated guidance such as that contained in Approved Document B: Fire safety, BS9999:2017 Fire Safety in the Design, Management and Use of Buildings and BS ISO 20414:2020 Fire Safety Engineering. Verification and Validation Protocol for Building Fire Evacuation Models.
It is key that the fire safety practitioner responsible for fire evacuation in a property as occupied has access to and can share necessary information in relation to the design of the means of escape are provided.
Although this information will not provide an exact evacuation time, it will enable:
This information is particularly important given the current emphasis on the “golden thread” of information approach for buildings that is recommended following a review into the Grenfell fire.
Human behaviour
It is widely recognised that up to two-thirds of actual evacuation time consists of occupants delaying when the evacuation signal is given.
These factors are built into what are known as the:
For safe evacuation to occur, the ASET must be significantly longer than the RSET. There are a number of factors that will affect the RSET and ASET. These include the time:
In theory the fire safety practitioner should be able to rely on the RSET and ASET and be confident that the evacuation time will be within this scope.
However, there are many factors that may affect the RSET and ASET in “real world” conditions, not least:
If occupants are unable to evacuate in a timely manner this could result in a breach of relevant fire safety legislation and increase the risk of injury or death.
PAS 79-1:2020 Fire Risk Assessment. Premises Other Than Housing. Code of Practice, notes that “an assessment should be made of the likely consequences of fire”.
The assessment should “understand that all persons within the premises should be able to reach a place of ultimate safety before life threatening conditions arise; either unaided or with the assistance of staff — without FRS assistance (RSET versus ASET)”.
In assessing this aspect, the fire risk assessor may consider a number of inputs into the process including:
These could then be used to determine (usually in a qualitative manner) whether the ASET/RSET requirements are being met or whether real-life evacuation takes longer, creating a situation where occupants may be at risk of harm.
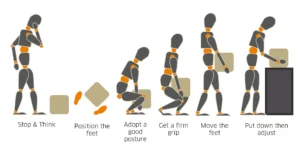 As workloads shift with the seasons, so do the risks we face. Now is a perfect time to reinforce safe manual handling practices and prevent musculoskeletal injuries across your team.
As workloads shift with the seasons, so do the risks we face. Now is a perfect time to reinforce safe manual handling practices and prevent musculoskeletal injuries across your team.
Whether you’re lifting, shifting, pushing, pulling, or simply standing for long hours—strains and sprains are the most common workplace injury in the UK. The good news? They’re also among the most preventable.
🤕 The Cost of “Just a Twinge”
We’ve all heard it: “It’s just a sore back—I’ll shake it off.” But injuries like:
Many of these injuries result from poor lifting techniques, rushing tasks, or using the wrong equipment.
🛠️ 5 Manual Handling Tips to Share with Your Team
📋 Don’t Forget: Employer & Employee Responsibilities
Under the Manual Handling Operations Regulations 1992, employers must:
Employees must:
✅ What Can You Do This Week?
👀 Remember: Good habits save backs, joints and time.
Small changes in how we lift, carry, and move can make a huge difference in injury prevention. Let’s keep sprains and strains off the sick list this summer.
Here is a toolbox talk to provide to staff – Click here Toolbox_Talk_Manual_Handling.
Contact us for further information.
April marks Stress Awareness Month a time dedicated to raising awareness about the causes and effects of stress, and more importantly, how we can take steps to manage it in our daily lives. Whether it stems from work pressures, personal challenges, or simply the fast pace of modern life, stress can take a serious toll on our wellbeing if left unchecked.
In this blog, I will be looking at the small changes we can make that will have a big difference on both our mental and physical health, and some practical strategies we can all use to reduce its effects both at work and at home.
Contact us for further information.
 WHY LACK OF SAFETY INDUCTION AND TRAININGS LEADS TO ACCIDENTS
WHY LACK OF SAFETY INDUCTION AND TRAININGS LEADS TO ACCIDENTS
Lack of Hazard Awareness
Without proper induction, workers may be completely unaware of the specific hazards present in their work environment.
This includes dangers related to machinery, chemicals, working at heights, and other potential risks.
Insufficient Knowledge of Safe Work Practices
Training provides essential knowledge of safe operating procedures, the correct use of personal protective equipment (PPE), and emergency response protocols.
Without this knowledge, workers are more likely to make errors that lead to accidents.
Failure to Recognize and Respond to Risks
Effective training teaches workers how to recognize potential hazards and how to take appropriate action to mitigate those risks. Lack of training leaves workers ill-equipped to handle unexpected situations.
Increased Risk of Human Error
Human error is a major contributing factor to accidents. However, proper training can significantly reduce the likelihood of errors by providing workers with the necessary skills and knowledge to perform their tasks safely.
Inadequate Emergency Preparedness
Safety induction and training include instruction on emergency procedures, such as evacuation plans and first aid. Without this training, workers may panic or make poor decisions in an emergency, exacerbating the situation.
Poor Safety Culture
When safety training is lacking, it creates a general poor safety culture. When workers and management do not prioritize safety, accidents are far more likely.
Super video to watch – Click Here
Any questions, please contact us.
 Do you know where your accident book is?
Do you know where your accident book is?
Accident books are a legal requirement.
More specifically, by law, every employer must record accidents to employees and visitors. Two key laws apply to accident reporting/recording at work:
Many people think that the accident book is a health and safety requirement. After all, accidents are a health and safety issue, and regulations that require the reporting of accidents (like RIDDOR) are health and safety regulations too.
So it might surprise you to find out that the law on accident books doesn’t come from a health and safety regulation. The SSCPR makes accident books a legal requirement for businesses employing 10 or more people.
So if you employ less than 10 people, you don’t legally need an accident book under the SSCPR. However, RIDDOR reporting is a legal requirement for businesses of any size, so it makes sense for every workplace to keep an accident book to comply with the law.
If an accident happens, the details of the accident and the injury should be recorded in the accident book.
Schedule 4 of the SSCPR lists the contents that should be entered into an accident book record as:
Accident book records must legally be kept for at least three years. However, it is good practice to keep them for at least 6 years in case of legal action.
The accident book, and any following investigation, can give a complete record of the accident should an insurance claim be made, and should also be seen as an opportunity to improve health and safety and prevent future accidents.
The accident book should be kept by the employer, but there are times when a record may need to be shared with others:
Most of the time, the details recorded in the accident book should be kept confidential and don’t need to be shared or reported to external services like the HSE. Things like minor accidents need to be investigated by the employer but don’t need to be recorded outside the organisation.
Contact us if you require further information.